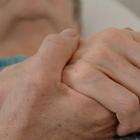
One in Three Alzheimer’s Cases Potentially Preventable, Study Says
July 14, 2024 12:02 pm | News | CommentsA third of Alzheimer’s disease cases worldwide can be attributed to risk factors that can be potentially modified, such as lack of education and physical inactivity, according to new research.
Gene Therapy Brings ALS Cure One Step Closer
July 11, 2024 12:44 pm | News | CommentsResearchers have moved one step closer to a gene therapy that could silence the faulty SOD1 gene responsible for triggering a form of motor neuron disease also known as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Scientists Shed New Light on Nerve Cell Growth
July 11, 2024 12:03 pm | News | CommentsIn a new study, scientists have shed new light on these complex processes, showing that a particular protein plays a far more sophisticated role in neuron development than previously thought.
Study Cracks How the Brain Processes Emotions
July 9, 2024 4:05 pm | News | CommentsAlthough feelings are personal and subjective, the human brain turns them into a standard code that objectively represents emotions across different senses, situations and even people, reports a new study by Cornell University neuroscientist Adam Anderson.
Huntington’s Disease Protein Helps Wire the Young Brain
July 9, 2024 12:07 pm | News | CommentsThe protein that is mutated in Huntington’s disease is critical for wiring the brain in early life, according to a new Duke University study. The new findings add to growing evidence that Huntington’s and other neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, may take root during development.
Cinnamon Could Halt Progression of Parkinson’s
July 9, 2024 10:26 am | News | CommentsNeurological scientists have found that using cinnamon, a common food spice and flavoring material, can reverse the biomechanical, cellular and anatomical changes that occur in the brains of mice with Parkinson’s disease (PD).
Dodging Dots Helps Explain Brain Circuitry
July 8, 2024 2:02 pm | Videos | CommentsA neuroscience study provides new insight into the primal brain circuits involved in collision avoidance, and perhaps a more general model of how neurons can participate in networks to process information and act on it. In the study, neuroscientists tracked the cell-by-cell progress of neural signals from the eyes through the brains of tadpoles as they saw and reacted to stimuli including an apparently approaching black circle.
Breaking News: Same Genes Drive Math, Reading Ability
July 8, 2024 11:00 am | News | CommentsAround half of the genes that influence how well a child can read also play a role in their mathematics ability, according to scientists who led a study into the genetic basis of cognitive traits.
Schizophrenia-associated Gene Variation Affects Brain Cell Development
July 7, 2024 2:46 pm | News | CommentsResearchers have begun to connect the dots between a schizophrenia-linked genetic variation and its effect on the developing brain. Their experiments show that the loss of a particular gene alters the skeletons of developing brain cells, which in turn disrupts the orderly layers those cells would normally form.
Scientists Find Key Piece in Brain Tumor Puzzle
July 7, 2024 11:22 am | News | CommentsScientists have shown that a member of the protein family known as SUMO (small ubiquitin-like modifier) is a key to why tumor cells multiply uncontrollably, especially in the case of glioblastoma.
Lead in Kids’ Blood Linked to Behavioral, Emotional Issues
July 2, 2024 9:17 am | News | CommentsEmotional and behavioral problems show up even with low exposure to lead, and as blood lead levels increase in children, so do the problems, according to new research.
Addiction Starts with an Overcorrection in the Brain
July 1, 2024 4:48 pm | News | CommentsThe National Institutes of Health has turned to neuroscientists at the nation’s most “Stone Cold Sober” university for help finding ways to treat drug and alcohol addiction. Brigham Young University professor Scott Steffensen and his collaborators have published three new scientific papers that detail the brain mechanisms involved with addictive substances.
Stem Cells Halt MS for Two Years
July 1, 2024 12:07 pm | by Cynthia Fox | Articles | CommentsAt 21, MS had Jennifer Molson “wheelchair bound.” But since her stem cell transplant, she has worked, driven, danced at her own wedding. The story had a room of 1,000 professional stem cell scientists sniffling loudly at the International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) meeting—said sniffling reaching a crescendo when the quiet, pretty Molson concluded: “I’m living proof stem cells can save lives.”
Sorting Out Emotions
July 1, 2024 10:54 am | News | CommentsBuilding on previous studies targeting the amygdala, a team of researchers have found that some brain cells recognize emotions based on the viewer's preconceptions rather than the true emotion being expressed.
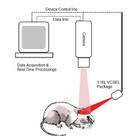
Watching Individual Neurons Respond to Magnetic Therapy
July 1, 2024 10:40 am | News | CommentsEngineers and neuroscientists have developed a method to measure the response of an individual neuron to transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) of the brain. The advance will help researchers understand the underlying physiological effects of TMS.
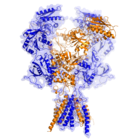
Research Gives 3-D View of Important Brain Receptor
June 30, 2024 12:02 pm | Videos | CommentsResearchers with Oregon Health & Science University's Vollum Institute have given science a new and unprecedented 3-D view of one of the most important receptors in the brain—a receptor that allows us to learn and remember, and whose dysfunction is involved in a wide range of neurological diseases and conditions, including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, schizophrenia and depression.
Early Life Stress Can Leave Lasting Impacts on the Brain
June 30, 2024 11:38 am | News | CommentsFor children, stress can go a long way. A little bit provides a platform for learning, adapting and coping. But a lot of it—chronic, toxic stress like poverty, neglect and physical abuse—can have lasting negative impacts. Researchers recently showed these kinds of stressors, experienced in early life, might be changing the parts of developing children's brains responsible for learning, memory and the processing of stress and emotion.
Potential Alzheimer’s Drug Prevents Abnormal Blood Clots in Brain
June 30, 2024 11:30 am | News | CommentsNew experiments have identified a compound that might halt the progression of Alzheimer’s by interfering with the role amyloid-beta plays in the formation of blood clots.
Noninvasive Brain Control
June 30, 2024 10:53 am | News | CommentsOptogenetics requires a light source to be implanted in the brain, where it can reach the cells that need to be controlled. Now, engineers have developed the first light-sensitive molecule that enables neurons to be silenced noninvasively, using a light source outside the skull.
Controlling Movement with Light
June 27, 2024 1:57 pm | News | CommentsNeuroscientists at MIT have shown they can control muscle movement by applying optogenetics—a technique that allows scientists to control neurons’ electrical impulses with light—to the spinal cords of animals that are awake and alert.
Running, Combined with Visual Stimuli, Restores Brain Function
June 27, 2024 1:04 pm | News | CommentsIn a new study, scientists explain that running, when accompanied by visual stimuli, restored brain function to normal levels in mice that had been deprived of visual experience in early life.
Insect Diet Helped Early Humans Build Bigger Brains
June 26, 2024 11:25 am | News | CommentsFiguring out how to survive on a lean-season diet of hard-to-reach ants, slugs and other bugs may have spurred the development of bigger brains and higher-level cognitive functions in the ancestors of humans and other primates, suggests new research.
Simultaneously Tracking Blood Flow, Oxygenation Can Revolutionize Neural Imaging
June 26, 2024 10:07 am | by Chris Ryan, Product Manager, QImaging | White PapersQuantifying brain activity through optical imaging has the potential to improve the way the biomedical community treats neurological disorders and brain injuries. To accurately visualize and treat patients who have suffered a stroke, epileptic attack or traumatic brain injury, neuroscientists require precise imaging and measurements of brain activity.
Gene in Brain Linked to Kidney Cancer
June 25, 2024 12:54 pm | Videos | CommentsA gene known to control brain growth and development is heavily involved in promoting clear cell renal cell carcinoma, the most common form of kidney cancer, researchers are reporting.
Fatal Cellular Malfunction Identified in Huntington’s Disease
June 24, 2024 1:28 pm | News | CommentsResearchers believe they have learned how mutations in the gene that causes Huntington’s disease kill brain cells, a finding that could open new opportunities for treating the fatal disorder. Scientists first linked the gene to the inherited disease more than 20 years ago.
- Page 1
- Next