FREE Email Newsletter Bioscience Technology Daily
Study Brings Universal Flu Vaccine a Step Closer
September 23, 2024 11:29 am | CommentsScientists have moved closer to developing a universal flu vaccine by using the 2009 swine flu pandemic to study why some people seem to resist severe illness. Researchers asked volunteers to donate blood samples just as the pandemic was getting underway and also asked the volunteers to report any symptoms they experienced over the next two flu seasons.
Tumors Caught Bursting Through a Blood Vessel
September 20, 2024 12:05 pm | CommentsResearchers at MIT have developed a microfluidic device that mimics the process of extravasation, showing the flow of cancer cells through a system of blood vessels. The extravasation process is a crucial step in cancer metastasis that, until now, has been unclear.
Bioscience Technology Update for September 20, 2024
September 20, 2024 11:46 am | CommentsIn this edition of Bioscience Technology Update: Surgeons Successfully Implant Bioengineered Vein Genetically Modified Mosquitoes Lose Appetite for Humans Bacteria Ingested Through Yogurt Affects Brain Function Young Genes Can Become Essential for Life
Healthy Lifestyle Can Lengthen Telomeres, Slow Aging
September 17, 2024 10:44 am | CommentsA small pilot study shows for the first time that changes in diet, exercise, stress management and social support may result in longer telomeres, the parts of chromosomes that affect aging. It is the first controlled trial to show that any intervention might lengthen telomeres over time.
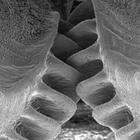
Functioning Gears Found in Nature for the First Time
September 13, 2024 11:17 am | CommentsPreviously believed to be only man-made, a natural example of a functioning gear mechanism has been discovered in a common insect- showing that evolution developed interlocking cogs long before we did. The juvenile Issus has hind-leg joints with curved cog-like strips of opposing “teeth” that intermesh, rotating like mechanical gears to synchronize the animal’s legs when it launches into a jump.
Embryonic Stem Cells Created in Adult Organism
September 12, 2024 11:49 am | CommentsA research team has become the first to make adult cells from a living organism retreat in their evolutionary development to recover the characteristics of embryonic stem cells. They have also discovered that these embryonic stem cells have a broader capacity for differentiation than those obtained via in vitro culture.
U.S. Faces Crisis in Cancer Care
September 11, 2024 1:09 pm | CommentsDelivery of cancer care in the U.S. is facing a crisis stemming from a combination of factors—a growing demand for such care, a shrinking oncology work force, rising costs of cancer care, and the complexity of the disease and its treatment, says a new report from the Institute of Medicine.
Inner-ear Disorders May Cause Hyperactivity
September 6, 2024 10:08 am | CommentsBehavioral abnormalities are traditionally thought to originate in the brain. But a new study has found that inner-ear dysfunction can directly cause neurological changes that increase hyperactivity. The study, conducted in mice, also implicated two brain proteins in this process, providing potential targets for intervention.
Stress-related Protein Speeds Alzheimer’s Progression
September 4, 2024 11:40 am | CommentsA stress-related protein genetically linked to depression, anxiety and other psychiatric disorders contributes to the acceleration of Alzheimer’s disease, a new study has found. When the protein FKBP51 partners with another protein, Hsp90, the team prevents the brain from clearing the toxic tau protein, associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
TB Has Surprising Family Tree
September 3, 2024 11:42 am | CommentsFor years, physicians around the world have watched as strain after strain of the deadly bacteria mycobacterium tuberculosis evolves resistance to drugs. A new method of analyzing whole genome sequences of TB, applied to a massive set of strains of the bacteria collected from clinics around the world, has revealed 39 new genes associated with elevated drug resistance.
Researchers Discover a Potential Cause of Autism
August 29, 2024 10:27 am | CommentsProblems with a key group of enzymes called topoisomerases can have profound effects on the genetic machinery behind brain development and potentially lead to autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Scientists at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine have described a finding that represents a significant advance in the hunt for environmental factors behind autism and lends new insights into the disorder’s genetic causes.
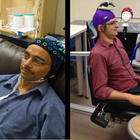
Researcher Controls Colleague’s Motions in First Human Brain-to-brain Interface
August 27, 2024 3:36 pm | CommentsResearchers have performed what they believe is the first noninvasive human-to-human brain interface, with one researcher able to send a brain signal via the Internet to control the hand motions of a fellow researcher, using electrical brain recordings and a form of magnetic stimulation.
Robots Remove Brain Blood Clots
August 9, 2024 10:25 am | CommentsSurgery to relieve the damaging pressure caused by hemorrhaging in the brain is a perfect job for a robot. That is the basic premise of a new image-guided surgical system, under development, that employs steerable needles to penetrate the brain with minimal damage and suction away the blood clot that has formed.
Real-time MRI Guides Gene Therapy to Tumors
August 7, 2024 10:08 am | CommentsNeurosurgeons from University of California, San Diego are among the first in the world to utilize real-time magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) guidance for delivery of gene therapy as a potential treatment for brain tumors. Using MRI navigational technology, neurosurgeons can inject a novel investigational gene therapy directly into a brain malignancy.
Celiac Intestinal Damage Ups Cancer Risk
August 6, 2024 10:31 am | CommentsPatients with celiac disease who had persistent intestine damage (identified with repeat biopsy) had a higher risk of lymphoma than patients whose intestines healed, according to a new study. The damage is due to a reaction to eating gluten, which is found in wheat, barley and rye.