FREE Email Newsletter Bioscience Technology Daily
Roomy Cages Built From DNA
March 14, 2024 1:38 pm | CommentsScientists at the Harvard's Wyss Institute have built a set of self-assembling DNA cages one-tenth as wide as a bacterium. The structures are some of the largest and most complex structures ever constructed solely from DNA. The scientists visualized them using a DNA-based super-resolution microscopy method — and obtained the first sharp 3D optical images of intact synthetic DNA nanostructures in solution.
What Happened When? How the Brain Stores Memories by Time
March 13, 2024 2:04 pm | CommentsBefore I left the house this morning, I let the cat out and started the dishwasher. Or was that yesterday? Very often, our memories must distinguish not just what happened and where, but when an event occurred—and what came before and after. New research shows that a part of the brain called the hippocampus stores memories by their "temporal context"—what happened before, and what came after.
Scientists ‘Herd’ Cells in New Approach to Tissue Engineering
March 12, 2024 1:24 pm | CommentsSometimes it only takes a quick jolt of electricity to get a swarm of cells moving in the right direction. Researchers found that an electrical current can be used to orchestrate the flow of a group of cells, an achievement that could establish the basis for more controlled forms of tissue engineering and for potential applications such as “smart bandages” that use electrical stimulation to help heal wounds.
Cancer Cells Don’t Engage in ‘Drunken’ Walks as They Spread Through the Body in 3D
March 11, 2024 1:41 pm | CommentsBecause of results seen in flat lab dishes, biologists have believed that cancers cells move through the body in a slow, aimless fashion, resembling an intoxicated person who cannot walk in a straight line. This pattern, called a random walk, may hold true for cells traveling across two-dimensional lab containers, but researchers have discovered that for cells moving through 3-D spaces within the body, the “drunken” model doesn’t hold true.
A Tale of Two Data Sets: New DNA Analysis Strategy Helps Researchers Cut through the Dirt
March 11, 2024 1:00 pm | CommentsFor soil microbiology, it is the best of times. While no one has undertaken an accurate census, a spoonful of soil holds hundreds of billions of microbial cells, encompassing thousands of species. Researchers have now published the largest soil DNA sequencing effort to date.
Blood Test Identifies Those at Risk for Cognitive Decline, Alzheimer’s Within Three Years
March 10, 2024 9:44 am | CommentsResearchers have discovered and validated a blood test that can predict with greater than 90 percent accuracy if a healthy person will develop mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer’s disease within three years. It is the first known published report of blood-based biomarkers for preclinical Alzheimer’s disease.
New Shrinking Gel Steers Tooth Tissue Formation
March 6, 2024 3:01 pm | CommentsA bit of pressure from a new shrinking, sponge-like gel is all it takes to turn transplanted unspecialized cells into cells that lay down minerals and begin to form teeth. The bioinspired gel material could one day help repair or replace damaged organs, such as teeth and bone, and possibly other organs as well.
The Benefits of Personalized Medicine: What Is It?
March 6, 2024 2:54 pm | CommentsPersonalized medicine is a term you hear a lot in life science and drug industry discussions. Follow along as Rob Fee, Editor-in-Chief of Bioscience Technology, introduces a six-part video series from Bioscience Technology and Drug Discovery & Development that will explain what personalized medicine is, how it works, and the potential of this concept.
A Bird's Eye View of Cellular RNAs
February 28, 2024 11:57 am | CommentsIn biology, as in real estate, location matters. Working copies of active genes—called messenger RNAs or mRNAs—are positioned strategically throughout living tissues, and their location often helps regulate how cells and tissues grow and develop. But to analyze many mRNAs simultaneously, scientists have had to grind cells to a pulp, which left them no good way to pinpoint where those mRNAs sat within the cell.
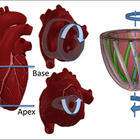
Artificial Muscles That Do the Twist
February 27, 2024 1:55 pm | CommentsIn the heart, as in the movies, 3D action beats the 2D experience hands down. In 3D, healthy hearts do their own version of the twist. Rather than a simple pumping action, they circulate blood as if they were wringing a towel. The bottom of the heart twists as it contracts in a counterclockwise direction while the top twists clockwise. Scientists call this the left ventricular twist—and it can be used as an indicator of heart health.
Zebrafish Discovery May Shed Light on Human Kidney Function
February 21, 2024 12:18 pm | CommentsResearchers say the discovery of how sodium ions pass through the gill of a zebrafish may be a clue to understanding a key function in the human kidney. The researchers discovered a protein responsible for gas exchanges in the fish gill structure. Specifically they studied and characterized the Na+/H+ (sodium/hydrogen) exchanger named NHE3, responsible for controlling sodium and hydrogen ions across the gill.
An Essential Step Toward Printing Living Tissues
February 20, 2024 11:55 am | CommentsA new bioprinting method creates intricately patterned 3D tissue constructs with multiple types of cells and tiny blood vessels. The work represents a major step toward a longstanding goal of tissue engineers: creating human tissue constructs realistic enough to test drug safety and effectiveness.
Researchers Develop Sticky Nanoparticles to Fight Heart Disease
February 19, 2024 2:05 pm | CommentsClemson University researchers have developed nanoparticles that can deliver drugs targeting damaged arteries, a non-invasive method to fight heart disease. One of the standard ways to treat clogged and damaged arteries currently is to implant vascular stents, which hold the vessels open and release such drugs as paclitaxel. The researchers hope their advanced nanoparticles could be used alongside stents or in lieu of them.
Baby Hearts Need Rhythm to Develop Correctly
February 19, 2024 1:08 pm | CommentsA team reports that they have taken an important step toward the goal of growing replacement heart valves from a patient’s own cells by determining that the mechanical forces generated by the rhythmic expansion and contraction of cardiac muscle cells play an active role in the initial stage of heart valve formation.
Method for Delivering HIV-Fighting Antibodies Proven Even More Promising
February 11, 2024 11:55 am | CommentsIn 2011, biologists at Caltech demonstrated a highly effective method for delivering HIV-fighting antibodies to mice—a treatment that protected the mice from infection by a laboratory strain of HIV delivered intravenously. Now the researchers, led by Nobel Laureate David Baltimore, have shown that the same procedure is just as effective against a strain of HIV found in the real world, even when transmitted across mucosal surfaces.